前言
本文同步发表在我的洛谷博客-01 字典树学习笔记。
但由于洛谷不允许在博客中添加外链图片,所以我们建议不要跳转至洛谷以便于获得更好的阅读体验。
Update on 2024.7.13:修正一处错误,感谢 skulker 的指出。
01 字典树
前置知识:字典树。
01 字典树是一种特殊的字典树,它会把数字看作二进制的 串存入字符串。
在树上,除了叶子节点外的所有节点都表示一个数的范围。
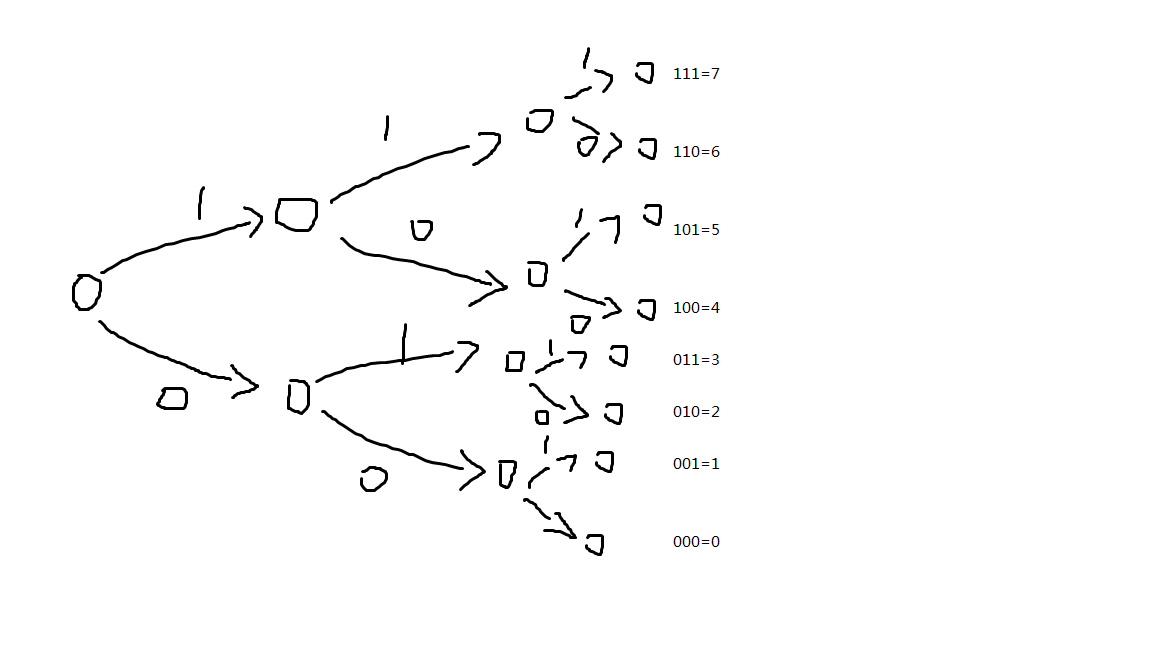
我们在插入元素时,和在字典树中插入元素时类似的。这里不再阐述。
插入示例代码如下:
const int MAXN = 2e6 + 5, MAXL = 31;
int tr[MAXN][2], cnt[MAXN], r = 1;
void insert(int x){
int u = 1;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (!tr[u][v]){
tr[u][v] = ++r;
}
u = tr[u][v];
cnt[u]++;
}
}
如果我们把每个节点表示的数字都存储下来,那么就会是这样:
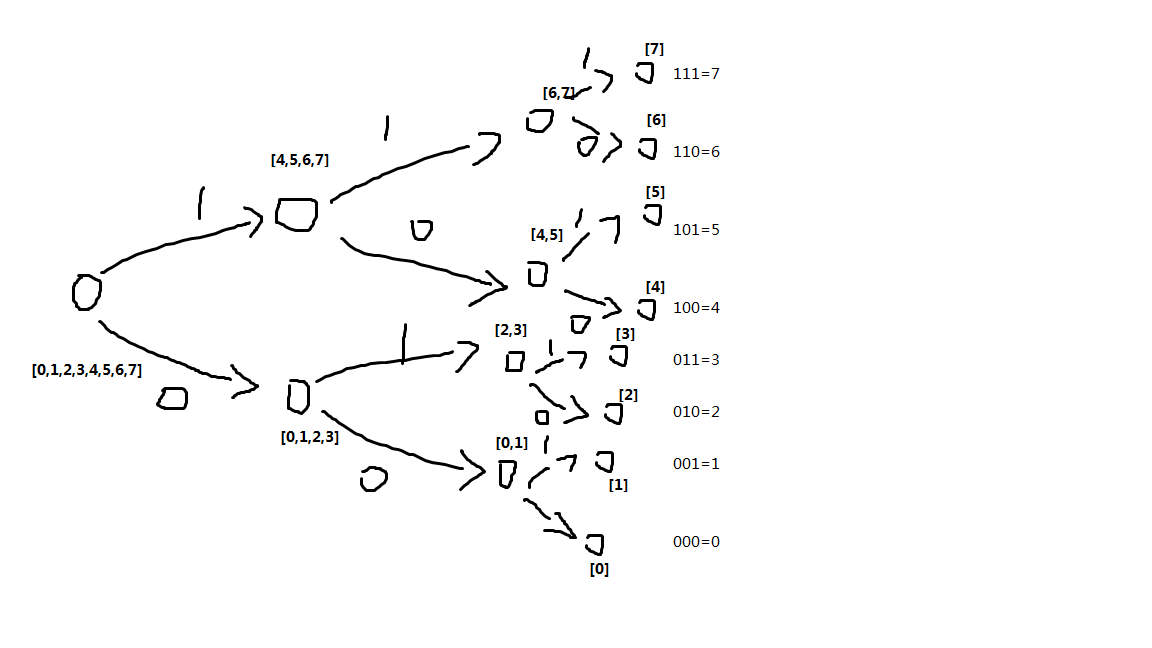
再修改一下,就变成了这样:
那么我们就可以发现:每个节点表示的数字都是一个区间。
那么 01 字典树能做些什么呢?它通常用来解决一些与位运算有关的问题。具体我们来看题。
当然,我们也可以使用 01 字典树以 的时间复杂度判断一个数字 是否出现过。相比于
map,常数会小很多。
例 1:洛谷 U77096 字典树|the xor largest pair
题意:给定 个正整数 ,求出
数据范围:。
本题我们就可以使用 01 字典树完成。
首先,对于异或来说,。
那么,如果我们想让这个异或值最大,对于 ,我们选择的匹配的数字的每一位就要尽可能的与 的对应位不同。
那么,我们在存储时记录下对应位置 中 0、1 的是否出现过,查找时尽量匹配与 对应位不同的数,最后对答案求最大值即可。
参考代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 7e6 + 5, MAXL = 31;
int tr[MAXN][2], r = 1, n, a[MAXN];
bool cnt[MAXN];
void insert(int x){
int u = 1;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (!tr[u][v]){
tr[u][v] = ++r;
}
u = tr[u][v];
cnt[u] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x){
int u = 1, ans = 0;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (tr[u][(v ^ 1)] && cnt[tr[u][v ^ 1]]){
u = tr[u][(v ^ 1)];
ans |= ((v ^ 1) << j);
}else if (tr[u][v] && cnt[tr[u][v]]){
u = tr[u][v];
ans |= (v << j);
}else {
return ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
insert(a[i]);
}
long long ans = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
ans = max(ans, 1ll * (a[i] ^ find(a[i])));
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
但是,如果这道题还增加了一个操作呢?那么就来到了下一题。
例二:CodeForces-706-D Vasiliy's Multiset
题意:有 次询问。初始序列 中只有一个数字 。每次询问属于以下三种操作之一:
1.+ x 表示将 加入序列 。
2.- x 表示将 从序列 中删除。如果序列中有多个 ,那么只删除一个。
3.? x 表示求出 。
对于每次询问 ,输出一个数表示答案。
数据范围:。
本题的其他实现与例 1 类似。但是增加了一个删除操作。
我们可以对 cnt 数组进行修改。从记录一个位置是否出现过改为一个位置出现过的次数。
删除操作就只要对对应位置的的出现次数减一即可。
参考代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 7e6 + 5, MAXL = 31;
int tr[MAXN][2], cnt[MAXN], r = 1;
void insert(int x){
int u = 1;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (!tr[u][v]){
tr[u][v] = ++r;
}
u = tr[u][v];
cnt[u]++;
}
}
int find(int x){
int u = 1, ans = 0;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (tr[u][(v ^ 1)] && cnt[tr[u][v ^ 1]]){
u = tr[u][(v ^ 1)];
ans |= ((v ^ 1) << j);
}else if (tr[u][v] && cnt[tr[u][v]]){
u = tr[u][v];
ans |= (v << j);
}else {
return ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
void del(int x){
int u = 1;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
u = tr[u][v];
cnt[u]--;
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int q;
cin >> q;
insert(0);
while (q--){
char s;
int x;
cin >> s >> x;
if (s == '+'){
insert(x);
}else if (s == '-'){
del(x);
}else {
cout << (x ^ find(x)) << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
例 3:HDU-6955 Xor sum
题意:有 组数据,每组数据给定一个长度为 的序列 。请你找出一个异或和不小于 的最短连续子串。
如果有多个满足要求的连续子串,输出左端点最小的。
如果不存在这样的序列,输出 -1。
数据范围:。
我们注意到,如果存在一个序列 ,那么有 。
也就是说,异或满足类似前缀和的思路。
所以,我们可以对序列 求前缀异或和,存储在数组 中。
此时,问题就转化为了:求两个数 ,要求 和 都最小,并且满足 。
现在,来考虑 insert 和 find 函数的实现。
我们可以把 数组记录的东西修改一下。因为我们要在满足条件的条件下使得在 一定的情况下 最大,那么我们就可以记录对应位置的 的最大值。
insert 函数的实现如下:
void insert(int x, int l){
int u = 1;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (!tr[u][v]){
tr[u][v] = ++r;
}
u = tr[u][v];
cnt[u] = max(cnt[u], l);
}
}
接下来是 find 函数。
首先我们需要让区间异或和 ,那么我们就看 的其中一个位数是 还是 。如果这一位是 ,那么我们在选择数字的时候就只能选择 。否则,、 都可以选择。
如果这一位是 ,那么对应位是 的一定满足答案的要求。此时就可以更新答案。
最后整合输出即可。
完整代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXV = 7e6 + 5, MAXL = 31, MAXN = 1e5 + 5;
int n, k, r = 1, t, tr[MAXV][2], a[MAXN], qz[MAXN], cnt[MAXV];
void insert(int x, int l){
int u = 1;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (!tr[u][v]){
tr[u][v] = ++r;
}
u = tr[u][v];
cnt[u] = max(cnt[u], l);
}
}
int find(int x){
int u = 1, ans = 0;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1, z = (k >> j) & 1;
if (z){
u = tr[u][(v ^ 1)];
}else {
ans = max(ans, cnt[tr[u][(v ^ 1)]]);
u = tr[u][v];
}
}
return max(ans, cnt[u]);
}
void Solve(){
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++){
tr[i][0] = tr[i][1] = cnt[i] = 0;
}
r = 1;
cin >> n >> k;
int ansl = -1, ansr = 1e9;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
qz[i] = (qz[i - 1] ^ a[i]);
insert(qz[i - 1], i);
int x = find(qz[i]);
if (x > 0 && i - x < ansr - ansl){
ansl = x, ansr = i;
}
}
if (ansl == -1){
cout << "-1\n";
}else {
cout << ansl << ' ' << ansr << '\n';
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while (t--){
Solve();
}
return 0;
}
例 4:洛谷-P3369 普通平衡树
题意:有 次询问,每次询问格式为 op x。具体含义如下:
- :插入数字 。
- :删除数字 。如果有多个,就只删除一个。
- :询问 的排名。一个数的排名为比它小的数字加一。
- :查询排名为 的数字。
- :求小于 且最大的数。
- :求大于 且最小的数。
数据范围:。
虽然这题叫做平衡树,但是我们也可以使用 01 字典树实现。
首先观察到 可以为负数,但 01 字典树不能使用负数,所以我们就整体加上偏移量 ,输出的时候再减去 即可。
操作一二没啥好说的,和上面的一样。
对于操作三,我们发现:如果当前位是 ,那么当前位是 的一定都小于当前数。答案累加即可。
代码如下:
void finda(int x){
int ans = 0, u = 1;
for (int j = 25; j >= 0; j--){
int v = (x >> j) & 1;
if (v){
ans += cnt[tr[u][0]];
}
u = tr[u][v];
}
cout << ans + 1 << '\n';
}
操作四和操作三差不多。代码如下:
void findb(int x){
int u = 1, ans = 0;
for (int j = 25; j >= 0; j--){
if (cnt[tr[u][0]] < x){
x -= cnt[tr[u][0]];
u = tr[u][1];
ans |= (1ll << j);
}else {
u = tr[u][0];
}
}
int p = 1e7;
cout << ans - p << '\n';
}
但是对于操作五和操作六呢?
我们可以发现:比 小且最大的数字的排名一定是 的排名减一。那么答案就是 findb(finda(x)-1)。
那么操作六也差不多。比 大且最小的数字的排名也就是 的排名加上 的出现次数 。那么答案就是 findb(finda(x)+p)。
当然操作五六也可以使用 multiset 进行维护。这里我们不在探讨。
最后,还是希望大家能把上面的四道例题消化好,在 OI 的道路上砥砺前行!